.jpg?imageView2/2/format/jp2)
1. The locking force of stainless steel is too large and the thermal conductivity is low, which is easy to cause the thread to be locked. Stainless steel nuts are heated due to friction during rotation. The thermal conductivity of stainless steel is relatively low. When the generated pressure and heat destroy the chromium oxide layer (the stainless steel oxide layer that is not easy to rust), the metal teeth will directly block/shear, and the stainless steel will become soft. Adhesion phenomenon
2. The inclination of the thread fit and the softness of stainless steel may cause jamming. During the installation process, uneven force or inclination will cause the central axis of the screw and nut to incline greatly, which is easy to damage the tooth profile and cause biting; if the iron is rubbed during the locking process, the hardness of the stainless steel screw is relatively soft.


 English
English  Español
Español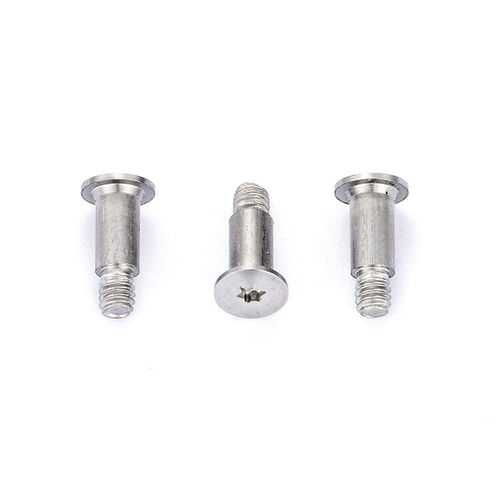
.jpg?imageView2/2/w/500/h/500/format/jpg/q/100)
.jpg?imageView2/2/w/500/h/500/format/jpg/q/100)
.jpg?imageView2/2/w/500/h/500/format/jpg/q/100)
.jpg?imageView2/2/w/500/h/500/format/jpg/q/100)
.jpg?imageView2/2/w/500/h/500/format/jpg/q/100)