Choosing the right
self-sealing screw for a specific application requires careful consideration of several factors to ensure a proper seal, durability, and overall functionality. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to make an informed selection:
Understand the Application Requirements:
Start by thoroughly understanding the requirements of your application. Consider factors such as pressure, temperature, fluid compatibility, load-bearing capacity, and environmental conditions.

Select the Sealing Element:
Determine the type of sealing element (e.g., O-ring, washer, gasket) that best suits your application. The choice will depend on the specific sealing requirements and the type of fluids or gases involved.
Material Compatibility:
Ensure that the material of the self-sealing screw and the sealing element is compatible with the fluids or gases in your application. Material compatibility is critical to prevent corrosion or degradation.
Size and Thread Type:
Choose the correct size and thread type for your self-sealing screw. Ensure that it matches the mating component's thread and fits securely.
Tightening Torque:
Determine the recommended tightening torque for the self-sealing screw. Over-tightening can damage the sealing element, while under-tightening can lead to leaks. Follow manufacturer guidelines for torque specifications.
Environmental Considerations:
Consider the operating environment, including exposure to chemicals, UV radiation, extreme temperatures, and moisture. Choose self-sealing screws with coatings or materials that provide protection against environmental factors.
Pressure Rating:
Ensure that the self-sealing screw is rated for the maximum pressure your system will experience. Using screws with a lower pressure rating can result in leaks or failures under pressure.
Temperature Range:
Verify that the self-sealing screw and sealing element can withstand the temperature range of your application. Extreme temperatures can affect the sealing performance.
Fluid Compatibility:
Check if the self-sealing screw and sealing element are compatible with the specific fluids or gases being used. Some materials may swell, degrade, or become brittle when exposed to certain chemicals.
Vibration and Shock Resistance:
If your application involves significant vibration or shock, choose self-sealing screws designed to withstand these conditions. Locking mechanisms or thread-locking compounds may be necessary.
Cost Considerations:
Balance the cost of the self-sealing screw with the performance and reliability it offers. While it's essential to stay within budget, prioritize quality and suitability for the application.
Consult with Suppliers or Manufacturers:
Documentation and Record-Keeping:
Maintain records of the self-sealing screws used in your application, including specifications, installation procedures, and maintenance requirements, to facilitate future replacements and inspections.
By carefully evaluating these factors and conducting thorough research, you can select the right self-sealing screw that ensures a reliable and long-lasting seal in your specific application.



 English
English  Español
Español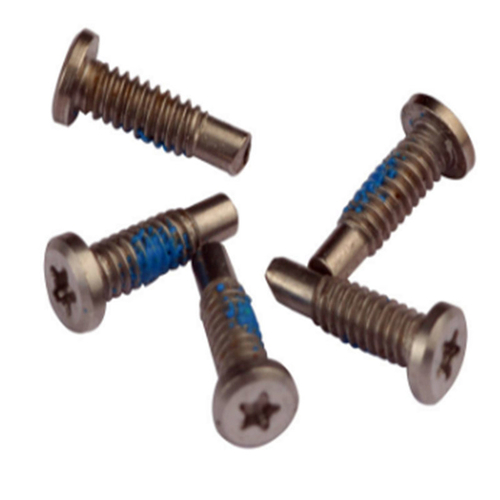
.jpg?imageView2/2/w/500/h/500/format/jpg/q/100)
.jpg?imageView2/2/w/500/h/500/format/jpg/q/100)
.jpg?imageView2/2/w/500/h/500/format/jpg/q/100)
.jpg?imageView2/2/w/500/h/500/format/jpg/q/100)
.jpg?imageView2/2/w/500/h/500/format/jpg/q/100)