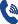
Tamper-resistant screws are designed with features that make them more challenging to remove without specialized tools, providing an additional level of security compared to standard screws. Here are key ways in which tamper-resistant screws differ from standard screws:
Unique Head Design:
Tamper-resistant screws have non-standard head designs that deviate from traditional Phillips, flat, or hex shapes. The unique head design requires a specialized tool for installation and removal, reducing the likelihood of tampering with common tools.
Security Features:
Tamper-resistant screws often incorporate security features such as center pins, recessed holes, or unique patterns that deter the use of standard screwdrivers or bits. These features make it more difficult for unauthorized individuals to access or manipulate the screws.
Specialized Tools Required:
Standard screws can typically be manipulated using common tools like Phillips screwdrivers or flathead screwdrivers. In contrast, tamper-resistant screws necessitate specialized tools, which are less commonly available. Examples include Torx drivers, spanner bits, pentalobe drivers, and other proprietary tools.
Tamper-Proof or One-Way Design:
Some tamper-resistant screws are designed to be tamper-proof or one-way. Once installed, they are challenging to remove without causing damage, preventing easy access by unauthorized individuals. This feature is often desirable in applications where permanent fastening is necessary.
Enhanced Security Levels:
Tamper-resistant screws are available in various security levels, offering different degrees of protection. Higher-security tamper-resistant screws may have additional features such as multiple pins, increased complexity in the head design, or enhanced materials to resist tampering attempts.
Security Applications:
Tamper-resistant screws are commonly used in applications where security is a priority, such as in electronic devices, appliances, public infrastructure, machinery, and certain types of access control systems. Standard screws are more prevalent in general-purpose applications.
Deterrence Against Tampering:
The primary purpose of tamper-resistant screws is to deter or delay tampering attempts. By requiring specialized tools and making it more challenging to access the screw head, tamper-resistant screws contribute to increased security and protection against unauthorized access.
Industry Standards and Compliance:
Certain industries, especially those with strict security requirements, may specify the use of tamper-resistant screws to comply with regulations or standards. Standard screws may not meet the security criteria required in such applications.
Cost Considerations:
Tamper-resistant screws are often more expensive than standard screws due to the specialized manufacturing processes involved in creating unique head designs. The increased cost is justified by the enhanced security they provide.
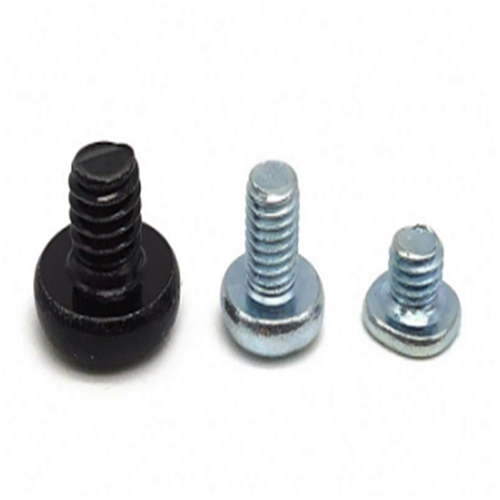
In summary, tamper-resistant screws differ from standard screws through their unique head designs, security features, the requirement for specialized tools, and their suitability for applications where increased security is essential. The choice between tamper-resistant and standard screws depends on the level of security needed and the specific requirements of the application or industry.
.jpg?imageView2/2/format/jp2)


 English
English  Español
Español

.jpg?imageView2/2/w/500/h/500/format/jpg/q/100)
.jpg?imageView2/2/w/500/h/500/format/jpg/q/100)
.jpg?imageView2/2/w/500/h/500/format/jpg/q/100)
.jpg?imageView2/2/w/500/h/500/format/jpg/q/100)